## The Relational Data Model --- ## Outline * Terminology * Relation Properties * Entity Relationship Model --- ## Relational Model * foundation of database research * foundation of many database design methodologies * foundation of structured query language (SQL) --- ## Domain * set of all atomic values that valid for an attribute * atomic: a value that is indivisible * e.g. the domain WorkDay is the set of {Mon,Tue,Wed,Thu,Fri,Sat,Sun} * e.g. HeadCount is the set of all non-negative integers * e.g. OutsideTemperature is the set of floating point values between -273.15 and 60 degrees C --- ## Domain * IceCreamFlavour? * CityPopulation? * PersonMass? --- ## Relation * also known as a table or file * named subset of the Cartesian product of a list of domains * given `$n$` domains denoted `$D_1, D_2, D_3, ..., D_n$` * relation `$R \subseteq D_1 \times D_2 \times D_3 \times ... \times D_n$` --- ## Attribute * also known as column or field --- ## Tuple * also known as row or record * values for attributes related to a single entity --- ## Degree * the number of attributes in a relation --- ## Properties of a Relation * a name distinct from other relations * no duplicate tuples * attributes within a tuple are atomic * values for an attribute come from a single domain --- ## Properties of Relation (continued) * operations combining data types is not allowed * each attribute has a distinct name * the order of attributes is insignificant * the order of tuples is insignificant --- ## Terminology Key |Formal Term (Codd)|Alternative #1|Alternative #2| |------------------|--------------|--------------| |Relation |Table |File | |Tuple |Row |Record | |Attribute |Column |Field | --- ## Entity Relationship Model --- ## Entity Relationship Model * approximately 50 years old * *entities*, tables that hold specific information * *relationships*, associations between entities --- ## Entity * object with physical existence (e.g. car, boat, student) * object with conceptual existence (e.g. account, job, ) --- ## Weak Entity * depends on another entity for its existence * its primary key includes the primary key of the parent entity * e.g. LineItem or OrderItem - depends on a corresponding Product --- ## Strong Entity * can exist on its own independent of related entities * kerenels are strong entities * a relation without a foreign key or where the foreign key can be null * e.g. Product relation --- ## Entity Type * defines a collection of similar entities --- ## Entity Set * collection of entities of an entity type at a particular point of time --- ## Independent Entities * also refered to as kernels * primary key may be simple or composite * primary key is not a foreign key * do not depend on any other entity for their existence --- ## Dependent Entities * also referred to as derived entities * used to connect two kernels together * existence dependence on two or more tables * many to many relationships, associative tables with at least two foreign keys --- ## Dependent Entities (continued) * options for primary key of dependent entity: * composite of foreign keys, if unique * composite of foreign keys and additional column(s) * create new simple primary key --- ## Characteristic Entities * represent multivalued attributes * describe other entities * typically have one to many relationship * foreign key is used to further identify characterized table --- ## Characteristic Entities (continued) * primary key options: * foreign key plus additional column(s) * create a new simple primary key --- ## Attributes * an entity is described by a set of attributes * attribute has a name, associated entity, domain of legal values ---  --- ## Types of Attributes * simple attributes * composite attributes * multivalued attributes --- ## Simple Attributes * come from atomic value domains --- ## Composite Attributes * consist of a hierarchy of attributes * e.g. "Address" has "Number", "Street", and "Suburb" parts --- ## Composite Attributes 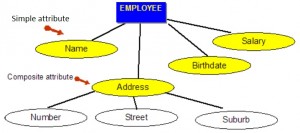 --- ## Multivalued Attributes * have a set of values for each entity * e.g. the "Degrees" attribute for an employee where an employee may have multiple degreees --- ## Multivalued Attributes 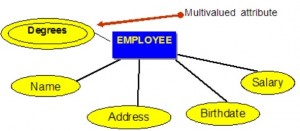 --- ## Derived Attributes * an attribute that can be calculated from other attributes * e.g. age can be derived from birthdate --- ## Derived Attributes 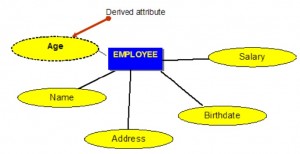 --- ## Keys * Candidate Key * Composite Key * Primary Key * Secondary Key --- ## Keys (continued) * Alternate Key * Foreign Key * Natural Key * Surrogate Key * Foreign Key --- ## Keys * an attribute or a group of attributes whose values can be used to uniquely identify and invidual entity in an entity set --- ## Candidate Key * simple or composite key that is unique and minimal * unique because no two tuples in the relaiton have the same values for the candiate key attributes --- ## Composite Key * composed of two or more attributes * must be minimal --- ## Primary Key * one candidate key selected by database designer to be the identifying key for the whole entity set --- ## Secondary Key * another key used strictly for retrival purposes --- ## Alternate Key * all other candidate keys --- ## Natural Key * a key made up of real world attributes * also known as a domain key or a business key * problematic if business rules change * e.g. assume (Name,Birthdate) is OK as a natural key for Employee but then hire another employee with same name and birthdate --- ## Surrogate Key * an invented attribute solely for the purposes for uniquely identifying tuples * also known as synthetic key or pseudokey * stable when business rules change * e.g. ??? --- ## Foreign Key * attribute(s) in a table the references the primary key in another table * the foreign key and corresponding primary key must be the same data type or domain --- ## Null * special value in all domains * means unknown or inapplicable or missing * distinct from 0 or blank * cannot be valid for a key attribute * can create problems for aggregate functions