## Relationships, Integrity Rules, and Constraints --- ## Outline * Relationships * Integrity Rules * Constraints --- ## Relationships * connections between related entities * used to connect related tables * may have thier own attributes --- ## Relationship Types * One to many (1:M) * One to one (1:1) * Many to many (M:N) * Unary (Recursive) * Ternary --- ## One to many (1:M) * one of one type of entity is related to multiples of another type of entity * e.g. on department has many employees --- ## One to many (1:M) 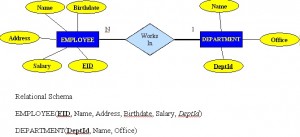 --- ## One to one (1:1) * one of one type of entityt is related to exactly one of another type of entity * e.g. one country has exactly one capital city --- ## Many to many (M:N) * one of one type of entity is related to multiples of another type of entity and vice versa * e.g. one employee works on many projects; a project has many employees working on it * typically implemented by a pair of one to many relationships --- ## Many to many (M:N) 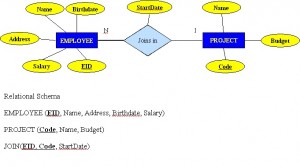 --- ## Unary (Recursive) * a relationship between occurrences of the same entity set * e.g. every employee has a manager (who is also an employee) --- ## Unary (Recursive) 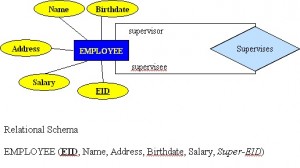 --- ## Ternary * a many to many to many relationship between 3 entities * typically impleneted by 3 one to many relationships --- ## Ternary 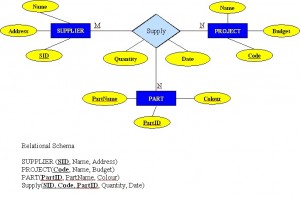 --- ## Integrity Rules --- ## Integrity Rules * Domain Integrity * Entity Integrity * Referential Integrity --- ## Domain Integrity * Domain identifies the universe of possible values for an attribute * often there additional constraints beyond the simple domain --- ## Entity Integrity * primary key cannot be NULL * primary key must be unique --- ## Referential Integrity * foreign key must match a primary key or be NULL --- ## Enterprise Constraints * additional rules beyond the basic integrity constraints * e.g.: * a class has a maximum of 30 students * an instructor teaches at most 4 courses * an employee's salary cannot exceed that of their manager --- ## Business Rules * additional rules discovered during requirements gathering * e.g.: * not all instrutors teach classes --- ## Cardinality and connectivity * Business rules specific to the maximum and minimum number of related entity occurrences (cardinality) * connectivity is the relatioship between two tables, e.g. one to one or one two many * connectivity can either be 0, 1, or many * cardinality and connectivity are represented together in a "crow's foot" diagram --- ## Instructor Course Example ```mermaid %%{init: {'theme': 'dark', 'themeVariables': { 'darkMode': true }, 'er': {'layoutDirection': 'LR'}}}%% erDiagram INSTRUCTOR ||--|{ COURSE : teaches ``` * an instructor teaches one or more courses * a course is taught by one and only one instructor --- ## Student Course Example ```mermaid %%{init: {'theme': 'dark', 'themeVariables': { 'darkMode': true }, 'er': {'layoutDirection': 'LR'}}}%% erDiagram STUDENT }|--|{ COURSE : enrolls ``` * a student enrolls in one or more courses * a course has one or more students enrolled in it